The BNMA BN Repository
This repository is a resource for posting and downloading Bayesian network models for sharing with others and for providing supporting material for publications. Please respect authors' rights where noted.
Search
73 BNs found.
The Lady Tasting Tea_extension

A cup of tea can be made in one of the two ways: the milk or the tea infusion was first added to the cup. The Lady Tasting Tea experiment consists in mixing eight cups of tea, four in one way and four in the other, and presenting them to the Lady for judgment in a random order. This short article presents a Bayesian Network (BN) for modelling the Lady Tasting Tea experiment that provides a comprehensive perspective in inferential analysis of all the data samples possibly generated from the experiment. More details of this BN model can be found in the article: <doi.org...>
Cryptocurrencies interconnectedness

This network illustrates the causal relationships between six cryptocurrencies, based on daily transaction data.
Predicting Age of Martens From Capture Data
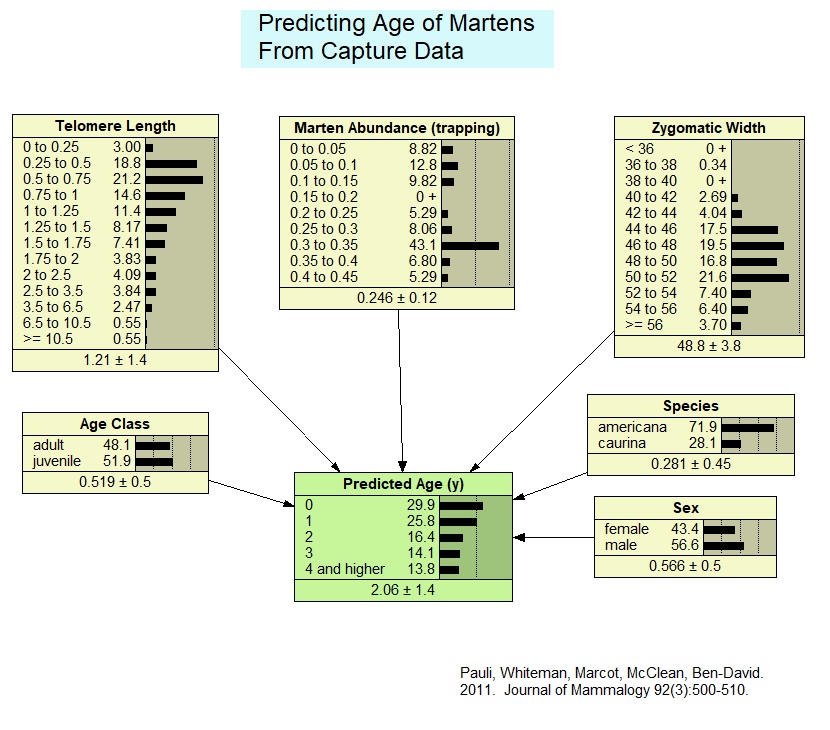
This model derives from a published version, slightly reformatted for testing an application of a Generative Adversarial Bayesian Network (GABN) framework. The model predicts the age of individual martens (members of the weasel family) based on six predictor attributes of marten sex, subspecies designation, zygomatic width (a measure of jawbone size), marten population density (derived from field trapping), telomere length (ends of the chromosomes that shorten over an individuals' life), and general age class (juvenile or adult). The model was initially parameterized with a case file of 399 samples of martens, and then used to generate a fictitious case file using Netica's "simulate cases" function, for testing the GABN approach.
GrapeGrower_reportV

This is a BN model developed from a questionnaire about the lived experience of grape growers in the Riverina, NSW 2022, Australia. The model structure specification was determined by following the novel sampling-subject-oriented approach (10.31235/osf.io/gqud3).
Polar Bear Stressor Model, Phase III (2023)

We revised a previous Bayesian network model to update projected 21st century polar bear population outcomes based on recent research findings on the species and newer Arctic sea ice projections by global climate models.
Assessing Environmental Injury - Reference Sites Only
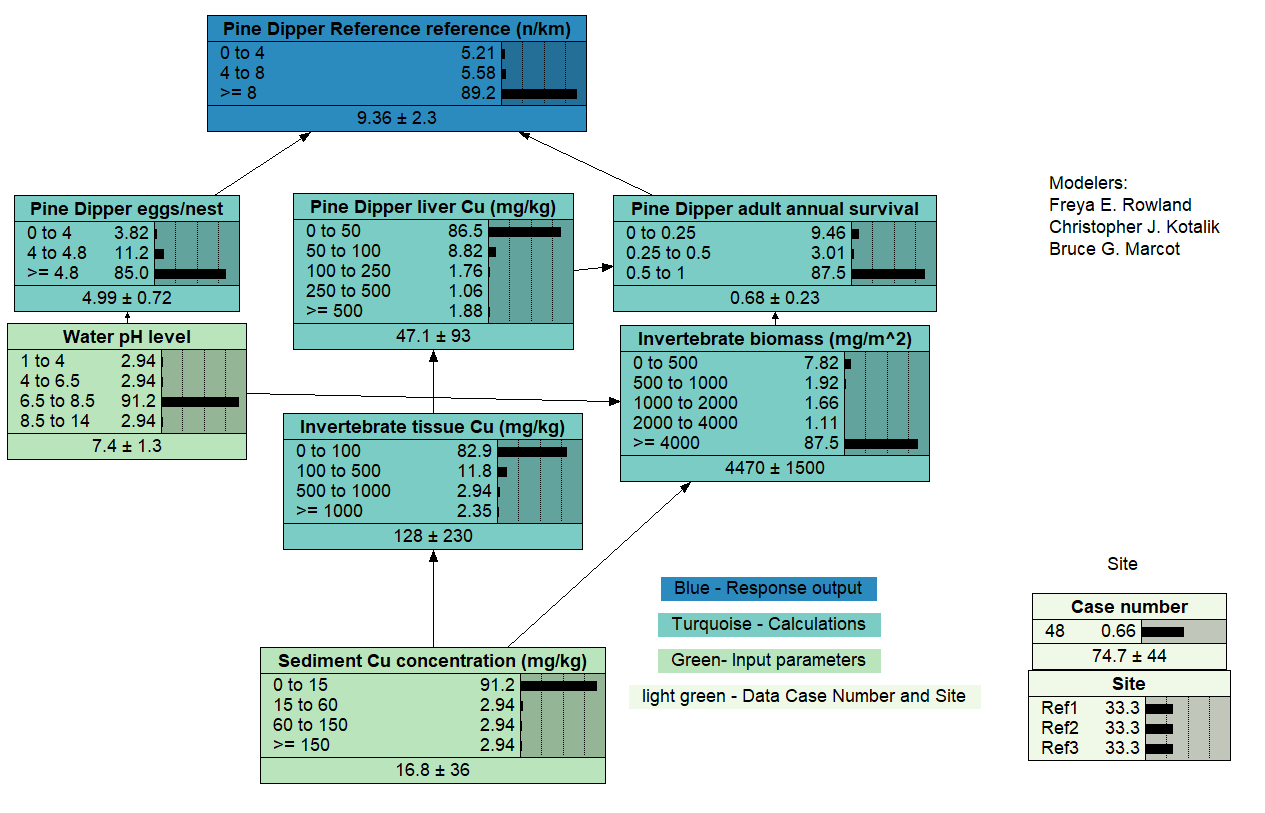
This model is a variant of the "Assessing Environmental Injury - Main Model", here for reference sites only, showing the probability of environmental injury on a hypothetical endangered bird species (Pine Dipper) that is potentially affected by stressors from acid mine drainage (AMD) source. The stressors here are copper (Cu) and water pH affecting the Pine Dipper directly and indirectly through macroinvertebrate prey. This was built for the Natural Resource Damage Assessment and Restoration (NRDAR) program in the U.S., and appears as Supporting Information Figure S1 in Rowland et al. (in press).
Assessing Environmental Injury - Main Model
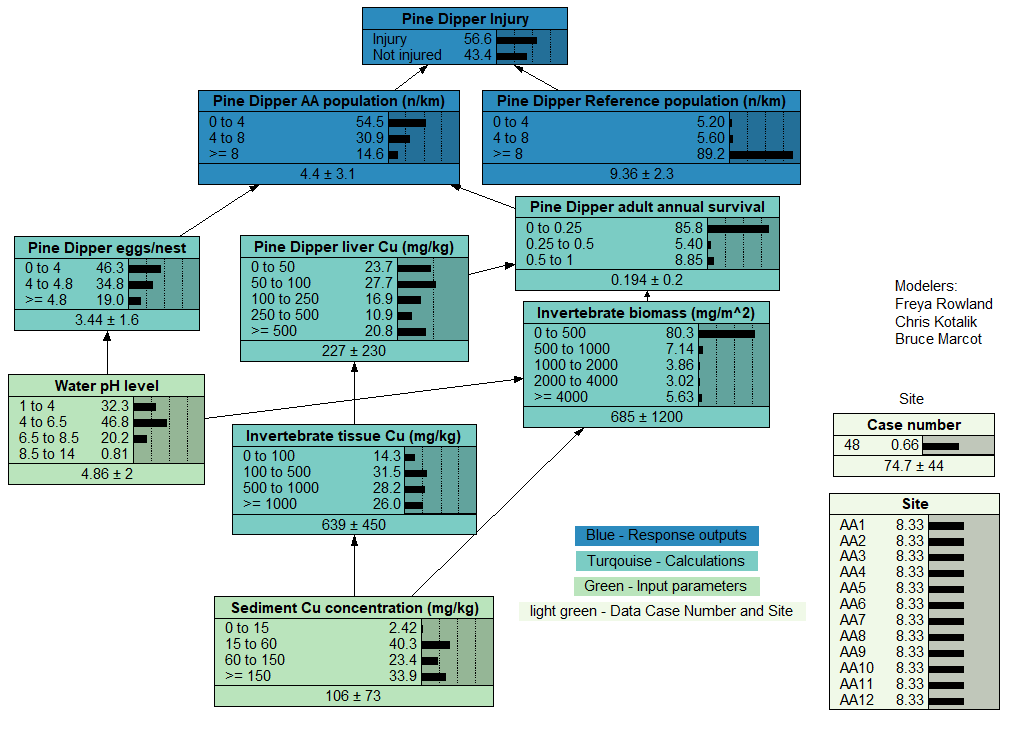
This model is a proof-of-concept example of how Bayesian networks (BNs) may be helpful in assessing natural resource injury within the Natural Resource Damage Assessment and Restoration (NRDAR) program in the U.S.
The data set for this model can be found at <abnms.org...>
Tidal Saline Wetlands

Predicts the loss of resilience of coastal tidal saline wetlands to a 1-5-m sea-level rise scenario along the Pacific Coast U.S.
The data set for this model can be found at <abnms.org...>.
Phytophthora_invasiveness_FINAL
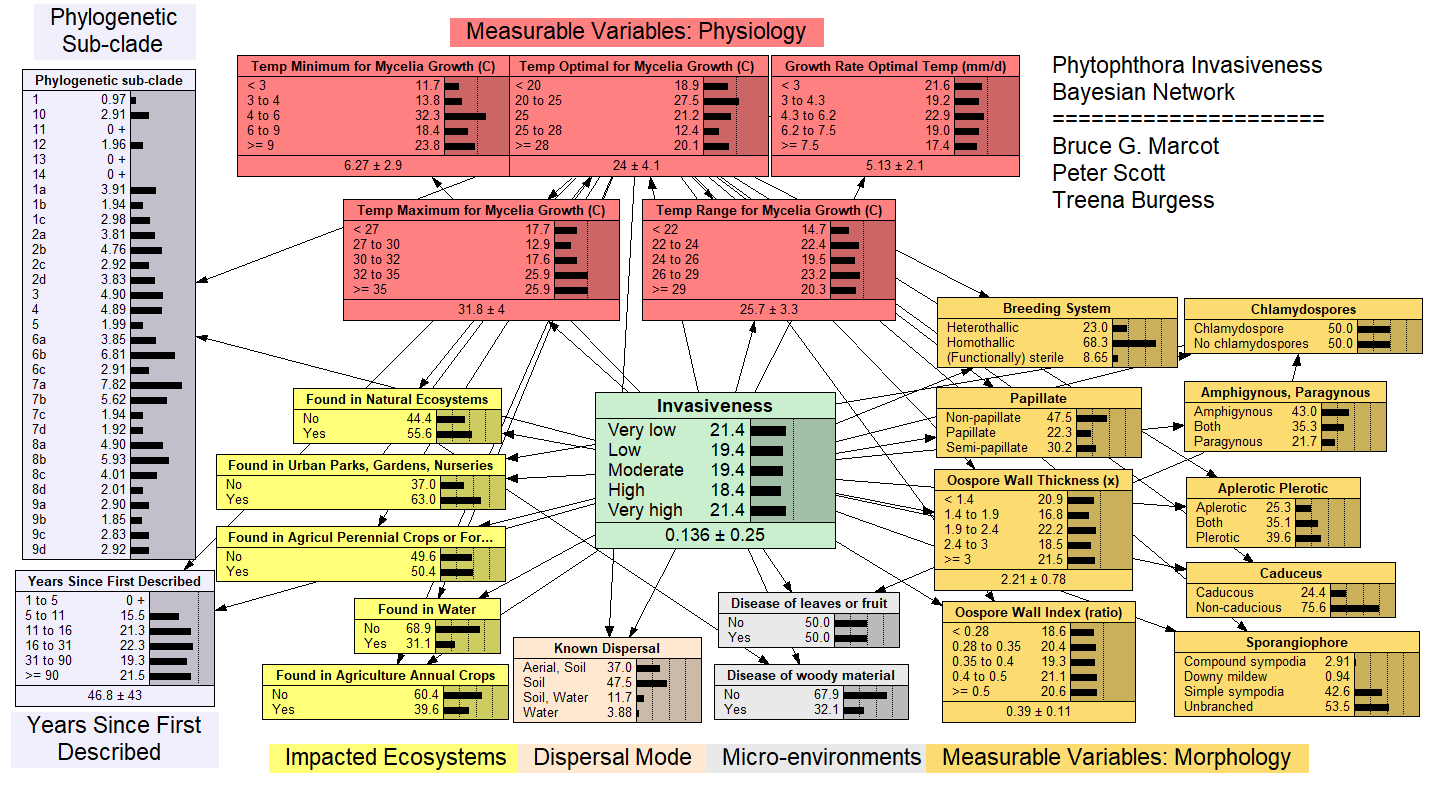
This model predicts the degree of invasiveness of species of Phytophthora, which are plant pathogens on native vegetation, agriculture, nurseries and urban parks and gardens.
Shark management survey analysis

In our recently published article “A scenario study of the acceptability to ocean users of more and less invasive management after shark-human interactions”, Bayesian Network (BN) was chosen as the principal analysis tool for identifying patterns from a study of 1769 valid responses from a survey which was open to all Australian residents aged 18 or over. The study was aimed to (1) Improve understanding of community attitudes in NSW to shark management options, and (2) Improve understanding of contextual influences on attitudes to shark bite mitigation approaches and how authorities should respond following an interaction. A modified BN model (26 nodes, 54 links) was proposed (implemented in Netica version 6.09) to improve the prediction performance of those four variables of risk management policy/strategy in the original BN model (26 nodes, 44 links) (implemented in Netica version 6.05)
BCA_Microctonus_NG_RiskAnalysis

BAIPA (for “Biocontrol Adverse Impact Probability Assessment”) is a new probabilistic tool that assesses the potential unwanted impact of organisms released in biological control programmes on non-target species.
The BN integrates information on the potential of an insect parasitoid used in biological control to: (1) disperse in new habitats; (2) interact with non-target species; and eventually (3) negatively impact the populations of the non-target species.
The two exemplar BNs on this repository assess the potential of an insect parasitoid released for biological control of pasture weevils in New Zealand (Microctonus aethiopoides) to disperse in new habitats, interact with on-target species (native weevils in the genus Nicaeana) , and eventually negatively impact the populations of the non-target species. Two habitats are assessed, low-intensity grazing pastures (LIP) and native grassland (NG - this model). Both models were built with GeNIe <bayesfusion.co...>
BCA_Microctonus_LIP_RiskAnalysis

BAIPA (for “Biocontrol Adverse Impact Probability Assessment”) is a new probabilistic tool that assesses the potential unwanted impact of organisms released in biological control programmes on non-target species.
The BN integrates information on the potential of an insect parasitoid used in biological control to: (1) disperse in new habitats; (2) interact with non-target species; and eventually (3) negatively impact the populations of the non-target species.
The two exemplar BNs on this repository assess the potential of an insect parasitoid released for biological control of pasture weevils in New Zealand (Microctonus aethiopoides) to disperse in new habitats, interact with on-target species (native weevils in the genus Nicaeana) , and eventually negatively impact the populations of the non-target species. Two habitats are assessed, low-intensity grazing pastures (LIP - this model) and native grassland (NG). Both models were built with GeNIe <bayesfusion.co...>
FISRAM Freshwater Species 190213

This model is used to determine the degree to which an introduced species of freshwater fish might be invasive and injurious. The model is used by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to help inform on species for potential exclusion of importation.
Arhopalus Flight Activity

This Bayesian network was developed to model the flight activity of Arhopalus ferus, a wood borer. The model is used to predict flight activity as a function of meteorological conditions. This contributes to the quantification of potential phytosanitary risks as it is a measure of potential exposure of export logs to flying/dispersing insects.
The data set for this model can be found at <abnms.org...>.
Hylastes Flight Activity

This Bayesian network was developed to model the flight activity of Hylastes ater, a bark beetle. The model is used to predict flight activity as a function of meteorological conditions. This contributes to the quantification of potential phytosanitary risks as it is a measure of potential exposure of export logs to flying/dispersing insects.
The data set for this model can be found at <abnms.org...>.
Hylurgus Flight Activity
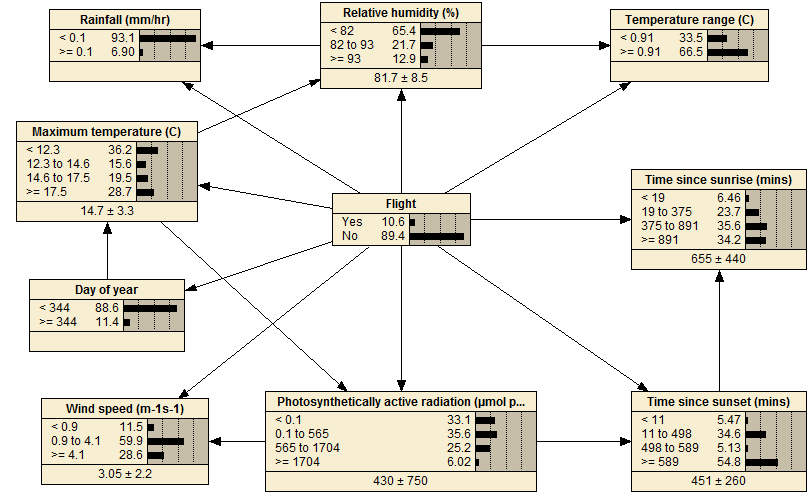
This Bayesian network was developed to model the flight activity of Hylurgus ligniperda as a function of meteorological conditions. H. ligniperda is a common forest insect within New Zealand Pinus radiata plantations forests. Predicting flight activity is one step towards assessing potential phytosanitary risks of forest exports as it is an indication of the exposure of logs to flying/dispersing insects.
The data set for this model can be found at <abnms.org...>.
iris

Simple classification network based on the classic Iris flower data set introduced by the statistician and biologist Ronald Fisher. The data set consists of 50 samples from each of three species of Iris (Iris setosa, Iris virginica and Iris versicolor). Four features were measured from each sample: the length and the width of the sepals and petals, in centimetres.
Refer: <en.wikipedia.org...>
Wet Grass

Many belief network researchers have used networks similar to this (possibly not containing nodes 'Neighbor's Grass' or 'Wall') to demonstrate "explaining away", and how rule based or evidence support systems may do incorrect chaining with these types of situations. For instance, they may combine the rules "If the ground is wet then it is likely it rained" with "If the sprinkler was on then it is likely the ground is wet" to get "If the sprinkler is on then it is likely it rained" when in fact the opposite is true. For example see Judea Pearl (1988) Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems, p. 7. The probabilities for this network were chosen by Norsys.
Paper link: <www.norsys.com...>
Thermostat A

A time delay decision network for the thermostat-heater control problem. This is a simple example of heater control, with a single heater, single thermal mass, single sensor, and costs for overheating, underheating, energy and switching the heater on and off. It could easily be expanded into a more complex example.
SpiegelhalterDLC93

A 20 node example of a belief net for medical diagnosis. This file does not contain the numerical probabilities (except those few given in the paper). This, together with the paper, provide a good worked out example for clique tree (i.e. join tree) compiling and propagation.
Paper link: <www.norsys.com...>
 Bayesian Intelligence
Bayesian Intelligence